
An Internet service provider (ISP) describes a company that provides customers with internet access from a computer. Data to access the internet are transmitted using several technologies, including dial-up, DSL, cable modem, wireless or dedicated high-speed interconnects.
The services may be unique to each ISP. An Internet service provider is also known as an Internet access provider (IAP). Your ISP makes the internet a possibility. In other words, you can have a computer with a modem but without a subscription with an ISP, you won’t have a connection to the Internet. An ISP is the main doorway to the internet and all that one can do online. The second you are connected to the internet and set up, you’ll be able to send emails, go shopping, do research and more. The ISP’s serves as a mediator between two different computers during the distribution of data and communication.
For instance, when you send an email to another email account, your email goes from your computer to the ISP computers/servers, where it’s sent along to its destination through other servers on the network. This path of transmission is an electronic path, therefore very fast.
TYPES OF INTERNET SERVICE PROVIDERS
ISP’s provide different services, these can be categorized into two main namely: Dial-up Service and Broadband Service (encompasses Digital subscriber line (DSL), Cable Broadband, Satellite and Fibre Optic service).
#1. Dial Up
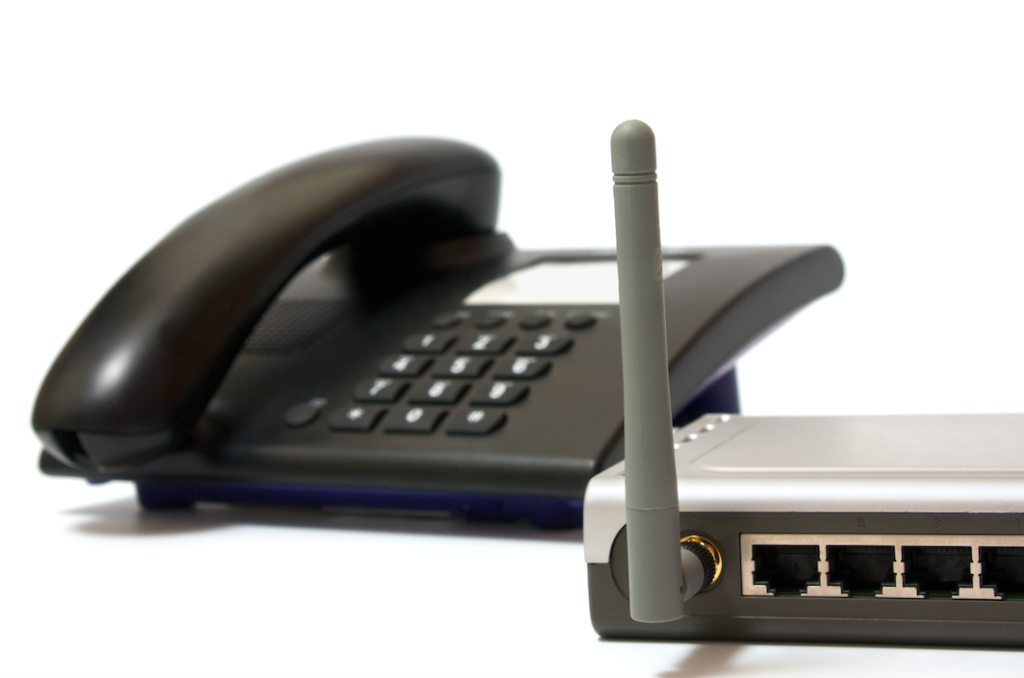

A dial-up connection allows access to the internet using a telephone line and analog modem, with data transfer rates (DTR) of up to 56 Kbps. A dial-up connection is the least expensive way to access the internet, but it also slowest connection. What most ISPs do is to provide you a set of telephone numbers either national or local that allows you to dial into a network that connects to the internet. This allows you to receive and send an email, browse the Web, participate in chat rooms and plenty of other features the web has to offer.
Broadband Internet service is the most used form of Internet access because of its high speeds; it is offered in four different forms, DSL (or Digital Subscriber Line), also fiber-optic, cable, and satellite.
#2. DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)

The DSL (or Digital Subscriber Line) internet service makes its connection using through copper wire telecommunication line with no interruption to your telephone service. The speed experience with a DSL connection varies with distance, thus the closer you are to the station the faster your internet speed. Along with cable internet, DSL is one of the most popular ways ISPs provide broadband internet access.
- It aims to maintain the high speed of the internet being transferred.
- DSL internet is a very cost-effective method and is best in connectivity
#3. Cable
The broadband cable connection is provided by the local cable TV provider. Here the internet connection varies depending on the number of users connected at the time. In a specific geographical area, for example, users of the broadband cable service share the connection bandwidth which slows the speed the more users are on the system. This will cause breaking and very slow internet speed especially in the evening when everybody is home and accessing the internet.
#4. Fibre Optic
This is the newest broadband, which is the fastest Internet connection thus far. However, this type of Internet service is still in its infancy stage as its service areas are quite limited and because the laying down of the fiber-optic cable takes a while to complete. The Fiber-Optic does not only compete with the DSL and cable in terms of cost, but also it provides a much faster connection than both of those services.
#5. Satellite
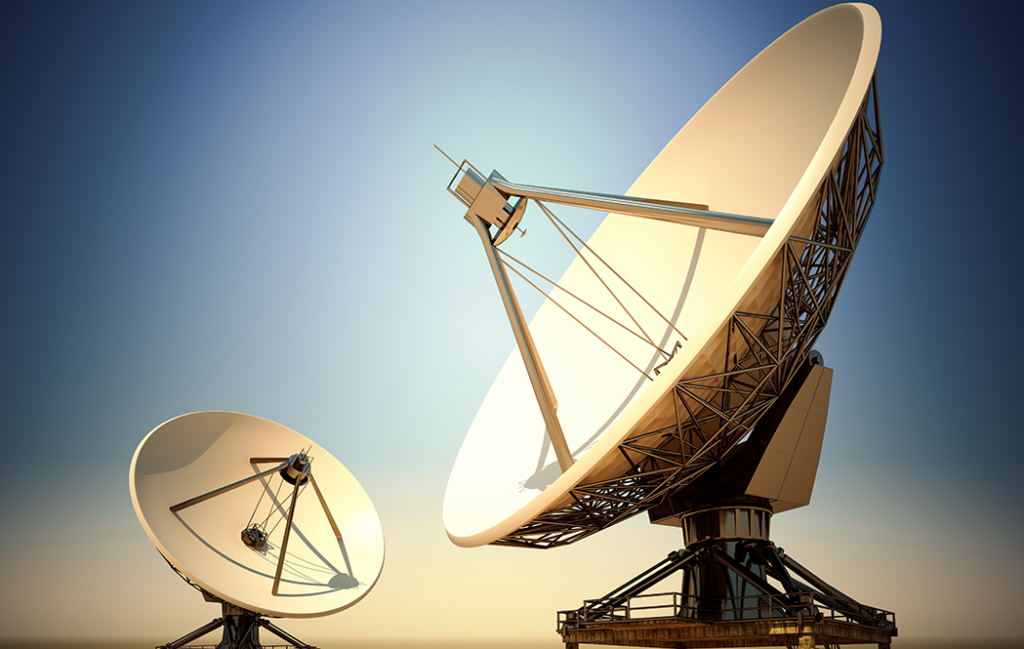

The last and slowest broadband service is provided by satellite. Although this is a good replacement for dial-up for those people living in remote rural areas, the installation costs are quite high, but the ongoing monthly charges are competitive to both cable and DSL. There are many advantages to the DSL and cable broadband service. It provides greater bandwidth than other Internet access forms, and that makes it easier for the computer user to multitask with several applications performing in the background while you surf the web. You can surf the web while listening to audio.
#6. Last Mile Wireless Connectivity
This is the telecommunication between the IPS and the users home or office without cables/wires. It is also called the CableFree Last-Mile Wireless Connectivity. It connects using Microwave, Millimeter Wave (MMW), Free Space Optics (FSO), MIMO Radio technologies. This technology has many advantages over the other types of Internet Connectivities.
- High speed and performance
- Low risks of Fibre cable breaks using wireless
- Rapid installation
- Safe & environmentally friendly

